Digital Innovation on Payor side platforms using API's, AI and beyond
Unlocking the Future: Harnessing the Power of APIs, AI, and Beyond for Payor Side Platforms' Digital Innovation
Introduction
The industry platform is a distinctive organizational form that has become significant over the past decades. Nowadays, a new digital platform together with its related ecosystem is positioned to create and capture value in digital economies.
With digital platforms, data is now a type of raw material and the basis for a new infrastructure used to generate revenue. In digital economies, with billions of consumers and providers connected through mobile online devices and engaging with other users almost continuously, platforms record and analyse enormous amounts of user-generated data, tracked via cookies and other services. Where there is data, there is value. Data and analytics are central to success in the platform business. But successful platform growth and scaling requires more data, more complex data, more variables, and more sophisticated analysis by more business people, beyond what can be done manually.
This post is sponsored by Health Compiler.
Unlock the full potential of your healthcare application with Health Compiler's comprehensive Health API. For a limited time, enjoy 20% off your purchase and take your healthcare technology to the next level.
The vast array of available digital platform data together with the rapid emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) insights and services have given rise to a perception of technology abundance. However, while most platforms have enough data processing solutions, products, and vendors, they are typically lacking a single organizational view into:
1) what AI transformation services they need to use, on
2) which digital assets, regarding
3) who, when, and why they should be provided, as well as
4) what services they should be integrating with, and
5) why they should be doing it.
Insights from the literature on platform enterprise architecture conceptualization are essential to understanding the relationship between platforms and AI innovation. In the era of Big Data (BD) and the privacy issues it raises, platform enterprises can ill afford to ignore runaway AI technology that may be collecting data outside the lines of industry and government regulations. Indeed, BD and AI present more than just a compliance risk.
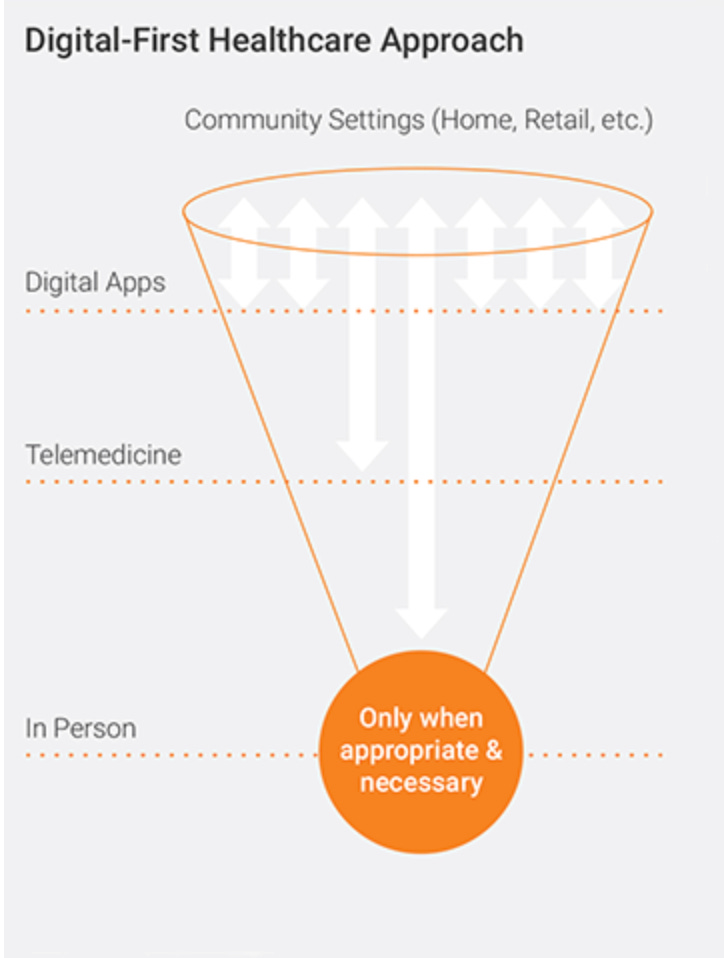
Pushing Healthcare Provision Outward with Digital Technology
Healthcare executives must move with urgency to adopt a digital-first strategy that transforms how the healthcare industry interacts with patients and members.
A digital-first approach to healthcare:
Expands capacity and accessibility through new channels of care
Makes possible comprehensive health and wellness initiatives in the community
Improves quality of care, reduces costs, and increases satisfaction through digital touchpoints
Provides personalized experiences for patients, members, and providers
What is AI-driven platform innovation?
What is the potential value of multilayer business platform AI innovation through a descriptive framework that combines AI with a digital platform stack?
AI disruption itself has a goal to drive better customer engagement and lead to accelerated rates of innovation, higher competitiveness, higher margins, and more productive employees. AI Awareness/Big Data Acquisition is the process of gathering, filtering, and cleaning data before it is put in a data warehouse, data lake, or any other storage solution on which data analysis can be carried out based on the availability of BD.
AI Decision Making/Big Data Usage covers data-driven business activities that need access to data, its analysis, and the tools to integrate data analysis as a business activity. It covers the main AI/BD assets usage in business decision-making that can improve competitiveness through reducing costs, increasing added value, or any other parameter that can be measured against existing performance criteria.
Digital platform transformation of enterprises across industries is still an emerging phenomenon. At a high level, digital transformation covers the intense changes taking place in society and industries through using digital technologies. At the organizational level, it has been contended that firms must find means to innovate with new technologies by creating “strategies that embrace the implications of digital transformation and drive better operational performance” .
AI-driven platform innovation can be developed through the lens described above involving business capability components and applications of a digital business platform technology stack they support. It is intended to provide a high-level overview of the key capabilities necessary to assemble a AI-driven platform innovation in the digital business platform stack.
Business Platforms
The Business Model and Leadership platform, as well as the Talent platform, are related more with platform capabilities. Their goal is to facilitate knowledge exchange in Business Model and Leadership environments and to offer affiliates the opportunity to access large intra-ecosystem or ecosystem communities of actors, with experiential, educational, or professional knowledge in a company’s diverse geographical and disciplinary fields. The key roles of a Business Model and a Leadership platform are to collect dispersed sources of knowledge, to recombine the collected knowledge, to empower innovation and management, and to transfer it to new technological and organizational contexts. Delivering a digital platform business requires new capabilities to enable, support, and manage digital business
The variance in a company’s digital business performance can be a function of the differences in their platform’s resources and capabilities compared with market competitors.
The Role of APIs In Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is increasingly propelled by rapidly changing user expectations. Release frequency is increasing, as is the need to connect a growing number of applications and digital experiences. As a result, 83% of IT specialists consider API integration critical to their business, found the State of API Integration Report.
APIs have become a standardized machine-readable mechanism for connecting partners. There is also a hot market for API start-ups, meaning APIs are becoming products in their own right. APIs are also enabling change for large enterprises. I recently connected with Bernd Gross, CTO at Software AG, to get his perspective on the role APIs and integrations are playing within the new wave of enterprise digital transformation. Below, we’ll see how connected customer experiences, digital business excellence and a new ecosystem-driven economy are driving the emergence of more API-based strategies.
Three Drivers of the Connected Enterprise
Businesses continue to transform into more connected enterprises. Once relegated solely to improving back-office efficiency, digitalization efforts are being applied across the board to employee management, assets, machines, partners and the supply chain at large, said Gross.
Amid rising digitalization, connectivity is the glue that unites disparate elements and tools.
Self-Service Integration With APIs
According to the report, 40% of companies said that digital transformation is driving their need for app integration. Truly connected enterprises must embrace digitalization and integration across all aspects of the business. As a result, this is forcing a business shift toward more open ecosystems.
But building these systems will require newfound knowledge dissemination around developer experience and self-service capabilities. “Self-service has become fundamentally important,” said Gross. It’s not enough to simply open interfaces — you have to also add self-service capabilities to integration tools, he added. This could mean offering low-code options alongside APIs — such drag-and-drop UIs would help facilitate integrations for more citizen developers.
The ability to manage APIs in such a way as to protect sensitive personal information is central to today's healthcare providers, so a basic understanding of what these superbly adaptable tools have to offer is important. For some time, healthcare productivity has lagged behind other sectors. In response to the consumerization of healthcare and outcome-based reimbursement systems, many organizations are now beginning to think in customer-centric terms. Existing business models in healthcare delivery and insurance are being disrupted by agile, cutting-edge public and private APIs.
API-Led Digital Transformation in Healthcare
The US healthcare industry is grappling with several issues, from surging costs and inefficient management to declining levels of care. The United States spends twice as much per capita on healthcare, yet lags behind other developed nations in patient outcomes. The good news is that leveraging digital transformation in healthcare can help overcome these challenges, with a staggering 92% of healthcare providers convinced of its effectiveness, according to a recent Deloitte study.
One of the most exciting breakthroughs in this regard is the adoption of APIs. APIs empower healthcare providers to leverage real-time data, helping them streamline operations, securely share data, and boost patient outcomes. Today, we’ll dive deep into API-led digital transformation in healthcare and discover how APIs are revolutionizing healthcare, benefitting patients, providers, and payors alike.
FHIR API and its role in interoperability
Short for Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources, FHIR is the main industry standard, developed for sharing healthcare data, specifically — Electronic Health Records. It utilizes the REST API architecture, implemented on HTTPS (HTTP Secure) protocol, and enables health systems to exchange data in JSON and XML formats.
The idea behind FHIR is to represent patient records as a set of resources, or separate data pieces of the same size and structure. Each resource has a unique ID and contains a small portion of information (say, a lab result or medication details). Depending on the query, the FHIR-based API retrieves a single resource or a combination merged in a larger document.
FHIR data model. Source: HL7 FHIR Release 4
Under the interoperability rules, healthcare providers and payers must implement FHIR to make certain elements of clinical and claims data available to patients via health apps.
However, it is expected that over time the standard will find widespread adoption across the entire industry, with all medical data structured as small, discrete resources.
EHR API: extracting data elements from health records
Data exposed: USCDI data elements and other patient information stored within one health IT system
What to build with them: patient-facing health apps, telehealth platforms, patient management solutions to track and monitor treatment plans, augmentation to existing patient portals.
Naturally, leading EHR vendors were first to comply with interoperability rules, long before they went into effect. Here, we’ll review FHIR resources from the EHR systems with the largest market share, namely
• Epic (29 percent),
• Cerner (26 percent),
• MEDITECH (17 percent), and
• Allscripts (7 percent).
Together, the Big Four spans almost 80 percent of US hospitals and health systems, so their APIs deserve closer study.
Telehealth and telemedicine are two terms often used interchangeably when speaking of remote care services. This includes but is not limited to patient data exchange, remote visits, appointment scheduling, and lab test ordering. Let’s look at some APIs designed with telehealth in mind.
Key Drivers of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Interoperability
Sharing patient data has been a significant challenge for healthcare providers, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Providers had to rely on manual methods such as phone calls, faxes, and emails to exchange patient information, which caused delays in diagnosis, treatment, and test results. Studies have shown that poor electronic health records (EHR) interoperability can also harm patients and increase healthcare costs.
Moreover, patients can have multiple healthcare providers, such as a primary care provider, a specialist, and a hospital. Each may use different EHR systems and store patient data in various formats. With 75% of hospitals having at least ten different EHRs on average, interoperability becomes significantly more challenging.
Evolving Patient Expectations
As digital healthcare technologies evolve, patient expectations shift towards greater control and personalization. Patients desire access to personal health data and the ability to communicate digitally with their healthcare providers. According to a recent survey by Statista, 70% of respondents are satisfied with using smartwatches to monitor their health.
To meet these evolving patient expectations, healthcare providers must adopt a more comprehensive approach to managing patient preferences. Providers must consider a patient’s lifestyle, environment, and social determinants of health when delivering care.
Providers who leverage digital healthcare technologies can offer more personalized and effective care and engage with patients more effectively. As such, healthcare organizations must prioritize healthcare transformation initiatives to remain competitive.
Shift towards Value-Based Care
Healthcare has been under pressure to transform its operating model. Issues such as patient dissatisfaction and concerns about the accessibility, payment, and coverage of health insurance warrant a change. Payors have shifted towards value-based care to meet patient demands for greater transparency regarding prices and access to EHRs.
The transition has been a significant trend in healthcare, with new investments growing faster than capital expenditures on new hospital construction, according to McKinsey.
The US government also incentivizes this shift by rewarding healthcare organizations transitioning from the traditional fee-for-service model to value-based care. These new programs encourage patient outcomes and quality care rather than the volume of services.
Therefore, healthcare providers and payors must prioritize patient-centered care and leverage real-time data for better clinical outcomes. APIs are enabling shift towards value-based care, driving several digital transformation initiatives in healthcare.
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
For Payors
Payors can leverage API-led transformation to improve operations and enhance services. APIs can help payors streamline claims processing, enabling faster payments and reducing the risk of fraud.
APIs help integrate claims data from various providers, creating a standard interface for gathering and processing claims data. Likewise, payors can streamline claims processing by seamlessly exchanging data from practice management and billing software.
As a result, your staff has real-time access claim information from any device or location, reducing administrative costs. Similarly, APIs can automate claim submissions and reduce the need for manual data entry, improving operational efficiency.
Providers also leverage API-based apps to engage with customers. They offer members access to their claims data, benefits information, and provider directories through secure portals and mobile apps. With this information, members can search for providers, check benefits, and track claims, empowering them to manage their healthcare more actively.
APIs can also help payors comply with HIPAA regulations and improve governance by enabling secure data exchange and management. Securely transmitting claims data between different healthcare systems can ensure that data is protected and managed in compliance with regulations.
For Patients
API-led transformation empowers patients to access their health data from anywhere, anytime, and via any device, enabling them to take a more active role in their care.
API-led transformation gives patients better access to their medical information through patient portals, mobile apps, or other online platforms. With greater patient engagement, patients can track their health status, set goals, and receive reminders for appointments and medication refills.
Health organizations can leverage the power of APIs to provide personalized care and improve patient outcomes. Ultimately, APIs empower patients by helping them take control of their health.
For Providers
API-led digital transformation offers a range of benefits for healthcare providers. APIs improve data sharing and interoperability between healthcare systems, enabling providers to integrate various EHR systems. As a result, providers have a holistic view of patient health and even gain real-time insights, helping them improve outcomes.
With remote monitoring and patient wearable devices, healthcare providers gain access to real-time patient data. This can help them keep track of vital health metrics remotely, enabling timely interventions.
With APIs, providers can also leverage real-time data to improve workflows. They can automate tasks like staff and appointment scheduling, improving efficiency, reducing costs and freeing staff time to improve care quality.
Developing APIs requires expertise in various technologies, such as REST, SOAP, and GraphQL. Additionally, ensuring that APIs work well with different systems and data sources can be time-consuming and require significant planning and coordination.
Security Risk
Healthcare data is sensitive, and APIs that expose patient data to unauthorized parties can pose significant risks. API security is crucial to prevent data breaches, and healthcare organizations must ensure that API access is secure and that patient data is protected.
Scalability and Maintenance
Embarking on an API-led digital health transformation journey requires significant investment. Financial costs aside, providers must hire skilled professionals who understand the nuances of healthcare IT.
The process of scaling and maintaining APIs can be complex and time-consuming, and healthcare organizations must have a clear strategy for managing their APIs to ensure that they remain scalable, maintainable, and up-to-date.
Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare is a highly regulated industry, and APIs must comply with various regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR, to ensure that patient data is handled appropriately. Therefore, healthcare organizations must ensure that their APIs comply with relevant regulations to avoid legal consequences.
These challenges underscore the importance of adopting a comprehensive strategy for implementing API-led digital transformations in healthcare. Healthcare organizations must prioritize API security, compliance, scalability, and maintenance to ensure the success of their digital transformation initiatives.
Conclusion:
Digital innovation powered by APIs, AI, and other advanced technologies has transformed payor-side platforms, revolutionizing the way healthcare payors operate. From seamless data exchange to personalized member engagement, these innovations offer significant benefits such as streamlined processes, reduced costs, and improved member experiences. As technology continues to evolve, payors must stay at the forefront of digital innovation to meet the changing demands of the industry and provide high-quality, cost-effective healthcare services to their members.